Microsoft Endpoint Management: ConfigMgr & Intune Licenses Combined
When it comes to Endpoint Management, organizations often wonder what the best approach is for their environment. The long and the short of it is there is no ‘one-size fits all’. In this blog we will explore what’s new, starting with the new unified ‘Microsoft Endpoint Management’, as well as how this can impact your current licensing and opportunities for your endpoint environment.
What is Microsoft Endpoint Management?
Endpoint Management, is Microsoft’s end-to-end management solution, combining the functionality of Microsoft Intune and Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager.
Whether you’re using desktops, laptops, smartphones, or tablets this type of solution ensures a simplified and secure location to govern them all. By using an Endpoint Management solution, you replace the need for disparate solutions for mobile device management, enterprise mobility management, and client management tools; thus, making the lives of your IT department much easier.
Have You Heard About Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
At the last Microsoft Ignite conference, Microsoft announced the release of “Microsoft Endpoint Manager,” unifying Configuration Manager (also known as ConfigMgr) and the Microsoft Intune mobile management service together. Microsoft Endpoint Manager is an integrated solution, allowing you to manage all of your devices. It includes both Configuration Manager and Intune, with no complicated configuration or migration required, and with much more simplified licensing. If you already have an existing investment in Configuration Manager you can continue to use it, while at the same time taking advantage of the Microsoft cloud-based security and compliance benefits of Intune.
According to Brad Anderson, Corporate Vice President of Microsoft 365:
“Microsoft Endpoint Manager is the convergence of Intune and ConfigMgr functionality and data – plus new intelligent actions – offering seamless, end-to-end management solution without the complexity of a migration or disruption to productivity.”
Handy, right? It’s essentially enabling customers to access everything they need, in just one place.
ConfigMgr & Microsoft Intune: Licensing with Endpoint Management
With the announcement of the Microsoft Endpoint Management platform, Microsoft has greatly simplified licensing. You now only require one license. By combining the two solutions (ConfigMgr and Intune), Microsoft has ensured the licensing to Intune is available to all ConfigMgr users and vice versa. This amendment has been made with the view of facilitating a more robust Endpoint Management solution for customers.
However, it should be noted, if you want to manage a non-Windows device (Android or iOS) through the Microsoft Endpoint Manager, you will need to purchase either:
- an Intune license;
- an Enterprise Mobility & Security (EMS) license;
- or a Microsoft 365 E3 or higher license.
Curious About Endpoint Management?
Check out our webinar ‘Endpoint Management: ConfigMgr, Intune or Both?’ to learn the ins and outs of Microsoft Endpoint Management from the experts!
Microsoft SCCM or Microsoft ConfigMgr?
Lesson #1: The Acronym Breakdown:
- SCCM – System Center Configuration Manager. Fun fact! Microsoft has never used or approved the use of this acronym, as the acronym SCCM is owned by the Society of Critical Care Medicine – check them out at sccm.org.
- ConfigMgr – Configuration Manager
Lesson #2: ConfigMgr, often referred to as SCCM, are synonymous.
Lesson #3: While commonly used, the acronym SCCM should not be used. Instead, we should use the acronym ConfigMgr, which is used to manage complex or large groups of devices running various Windows desktop and laptop operating systems on-premises.
In one central location, authorized users can manage PCs, servers, mobile devices, and virtual machines. Also, ConfigMgr allows administrative users to give end-users access to devices and applications they need without compromising on the company’s security.
ConfigMgr: When to Use & The Benefits
There are various features and capabilities of ConfigMgr that enterprises may find beneficial and useful. A few notable features include patch management, operating system deployment and remote control. Generally, Microsoft ConfigMgr begins to provide benefit when a business has 300 or more computers.
Below we have listed our top 3 benefits of using ConfigMgr:
- ConfigMgr provides smooth integrated device management, across mobile, physical, and virtual Windows OS environments, through a unified infrastructure.
- When teamed with Intune and Co-management, ConfigMgr offers enhanced visibility and enforcement options needed to maintain system compliance, whilst also making the administration of client systems much easier.
- When teamed with Intune and Co-management, not only does ConfigMgr give administrators the ability to protect corporate information, but also allow employees to reach applications they need in order to stay productive.
One key benefit of ConfigMgr is the streamlined deployment of Microsoft Windows workstation and Microsoft Windows server systems. Powerful task-sequence processing provides administrators with fine-grained control over the end-to-end OS deployment process. Combined with extensive reporting, simplified control of update deployment, and reliable application experiences, there are many reasons why ConfigMgr continues to make sense for corporate administrators.
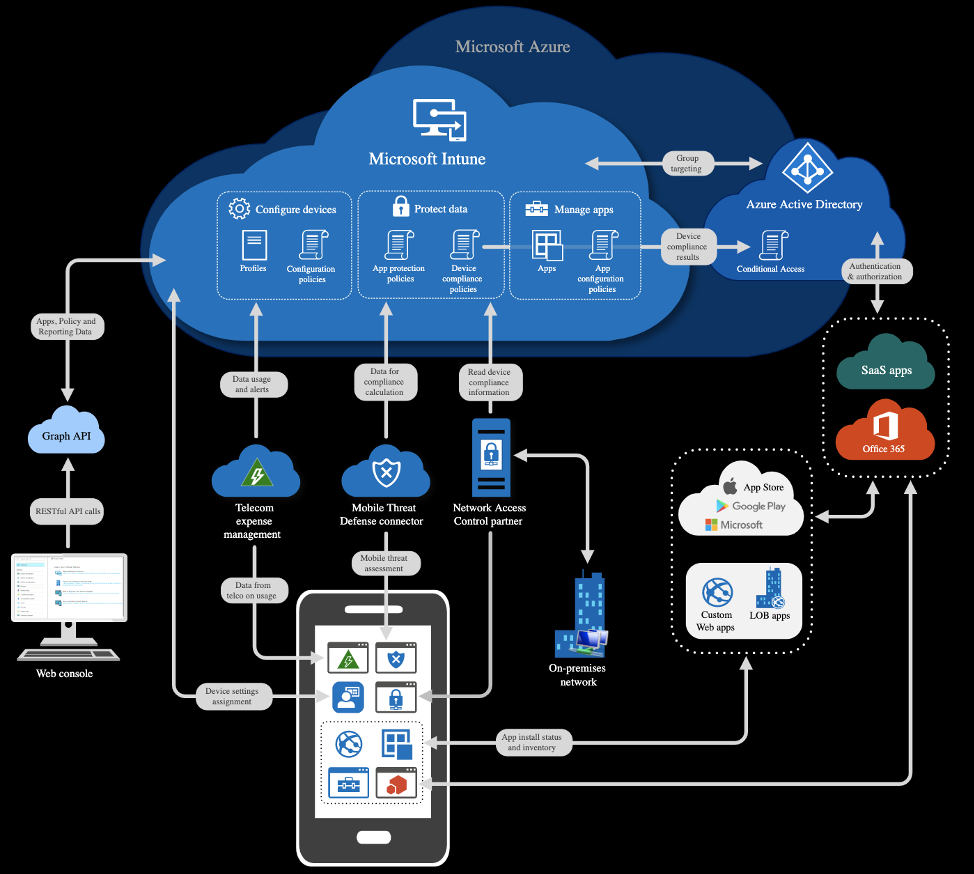
Where Does Microsoft Intune Come Into Play?
According to Microsoft, Intune is:
“a cloud-based service that focuses on mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM). Intune is included in Microsoft’s Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) suite and enables users to be productive while keeping your organization data protected.”
With Intune, organizations can manage both organization-owned and personal devices as well as bring-your-own-devices (BYOD). Licensed Intune users can enroll a device, either corporate or personal, for Intune management without requiring administrative credentials.
For organization-owned devices, you might decide you want full control over security, features, and settings. To facilitate this, the device is “enrolled” in Intune. Once set up, the device will receive the configurations and settings through policy configuration. An example might be – setting a password or PIN requirement, but you can do so much more.
For personal devices, or BYOD, users may not want their organization administrators to have full control over their equipment, so this pathway gives users more options as companies can decide to manage the entire device including all data and settings, or only to manage settings and configuration for corporate data.
All of this is in a bid to improve productivity and enable workforces to continue working from their devices while keeping company information secure. If a device is lost or stolen, the entire device can be wiped remotely from the Endpoint Management console. If a user leaves the company, all corporate data can be removed from the device without affecting the user’s personal apps and data.
FREE WEBINAR – Endpoint Management: ConfigMgr, Intune or Both? Webinar.
Find out more here >>
Microsoft Intune: When to Use & Benefits
Identifying when to use Intune for your organization is an important part of the planning process for a successful Intune installation. First, it helps to segment your users into manageable groups perhaps by:
- User type
- Role
- Ownership of the user’s device (company-owned or personal)
A good starting point, as with most things, is to refer to your organizational goals and objectives, as this helps identify the main use-case for deployment on Intune. The next step is to clarify the answers to the following –
- Are you planning to support corporate-owned devices, fully managed by the company?
- Are you planning to allow access to your corporate email and files from personally owned devices (BYOD)?
Quite often, you’ll find it’s not an either/or answer and you’ll need to support both forms of ownership to meet organizational needs. Once this is established within Microsoft Intune, you can:
- Secure your organization’s information by managing the way users access and share knowledge.
- Install apps on devices for both on-premises and mobile.
- Confirm devices and apps are compliant with company security.
- Set regulations and settings for personal and company-owned devices; who and what has access to data and networks.
Intune is beneficial for a number of reasons, but here are a few of the favorite reasons to use Intune:
- Sustain a varied mobile ecosystem: Reliably manage personal and company-owned devices from a unified source.
- Streamline your IT capabilities in the cloud: Increase your time-to-business value by utilizing a scalable, global, cloud product that’s always up to the minute.
- Protect data with or without Intune enrollment: Design policies and configure apps that keep organizational information safe without taking over the user’s device.
What are the Risks Involved in Using Both ConfigMgr & Intune?
Prior to Microsoft Endpoint Manager, ConfigMgr and Intune could be used as standalone products or as a hybrid. This came with a few limitations as customers were often confused about which system to use. In addition to this, users were concerned by the fact that Microsoft’s development innovations were delivered faster to organizations using the standalone Intune service compared to those utilizing the hybrid. Although this was likely due to Microsoft noting the importance of mobile in a rapidly evolving device orientated world.
Essentially this hybrid ConfigMgr implementation provided a steep learning curve. With Microsoft Endpoint Manager, along with the updated approach to licensing, Microsoft has brought together the two Endpoint Management products into a unified Endpoint Management Solution.
To conclude, Microsoft Endpoint Manager has been developed to make managing a variety of devices easier, while protecting organizational data, and allowing workforces to do their jobs via both corporate-owned and personal devices.
By combining both solutions; ConfigMgr and Intune, without the need for a complicated migration process, and newly streamlined licensing; Microsoft customers are able to leverage their existing ConfigMgr investments while taking advantage of what the Microsoft cloud has to offer.
Interested to find out more about Microsoft Endpoint Manager? Check out our ‘Endpoint Management: ConfigMgr, Intune or Both?’ webinar. Find out more here >>
Author: Doug Griffin
 Doug Griffin is an experienced Endpoint Management & Mobility Architect at Steeves and Associates. With a focus on System Center Configuration Manager since 1998 as well as Microsoft InTune, there are few in the field that has more hands-on experience. Doug Griffin also holds a wealth of certifications from Microsoft, including MCSA, MCTS, MCITP and is a Microsoft Certified Trainer. Griffin also has a Bachelor of Science from the University of Saskatchewan and over a decade of experience as an MCT, providing classroom and online-based training in ConfigMgr and other Microsoft products. In his time off, Doug enjoys playing Squash, although after years of practice he is still not very good at it.
Doug Griffin is an experienced Endpoint Management & Mobility Architect at Steeves and Associates. With a focus on System Center Configuration Manager since 1998 as well as Microsoft InTune, there are few in the field that has more hands-on experience. Doug Griffin also holds a wealth of certifications from Microsoft, including MCSA, MCTS, MCITP and is a Microsoft Certified Trainer. Griffin also has a Bachelor of Science from the University of Saskatchewan and over a decade of experience as an MCT, providing classroom and online-based training in ConfigMgr and other Microsoft products. In his time off, Doug enjoys playing Squash, although after years of practice he is still not very good at it.

